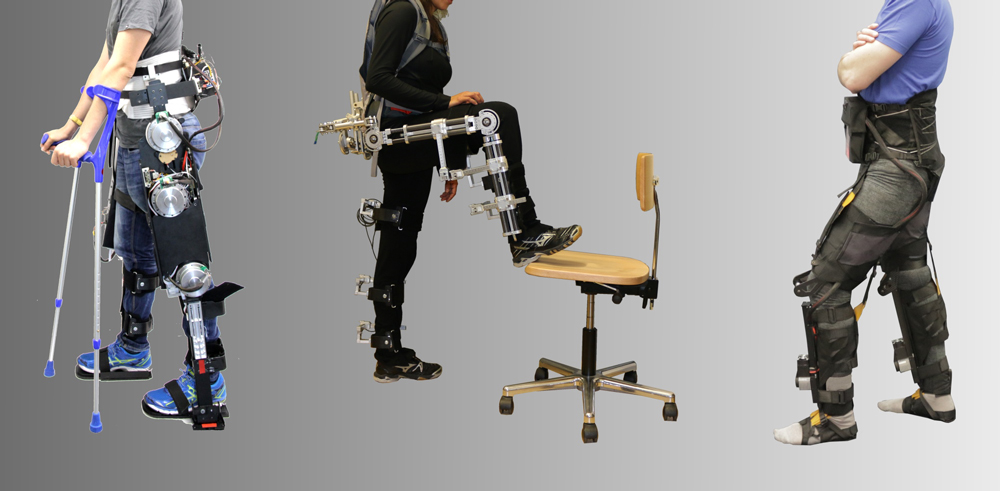
Lower Limb Exoskeletons and Exosuits
Our lower limb robotic exoskeleton research focuses on the development and evaluation of devices for gait rehabilitation and mobility assistance. We investigate physical human-exoskeleton interaction in order to identify limiting factors. We then translate these findings into novel designs of versatile, rigid exoskeletons and novel soft exosuit approaches. By addressing existing limitations, we aim to improve the performance and acceptance of exoskeletal devices and their application in daily life.
Our approach is to develop assistive and rehabilitation lower limb exoskeletons and exosuits that provide a defined and optimized support while reducing the constraints imposed by the system to increase the overall performance. Versatile research prototypes allow us to test new aspects and components and to evaluate new exoskeleton designs.
Subprojects
VLEXO – Exoskeleton Research Platform
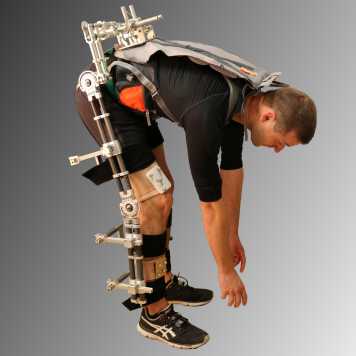
The mobile, passive VLEXO (versatile lower limb exoskeleton) is our current research platform to develop and evaluate new exoskeleton components. It allows for a simple alteration of its kinematic structure (number and kind of DOFs), dynamics and mechanical interfaces to investigate how different configurations affect the user. Aim of the project is to develop and evaluate ergonomic exoskeleton structures that can be used in different future systems.
Modular Lower Limb Exoskeletons

The reconfigurable exoskeleton is a feasibility and design study of a modular lower limb exoskeleton that can be adapted on a mechanical level to the intended user group and application. The introduced modular design allows to compose lower limb robotic exoskeletons with up to four degrees of freedom per leg. To each joint, a module can be added to define the functionality. Three different modules are introduced: one actuator for active support and two different adjustable spring modules that stabilize the joint around an equilibrium position.
Lokomat Gait Rehabilitation Robot
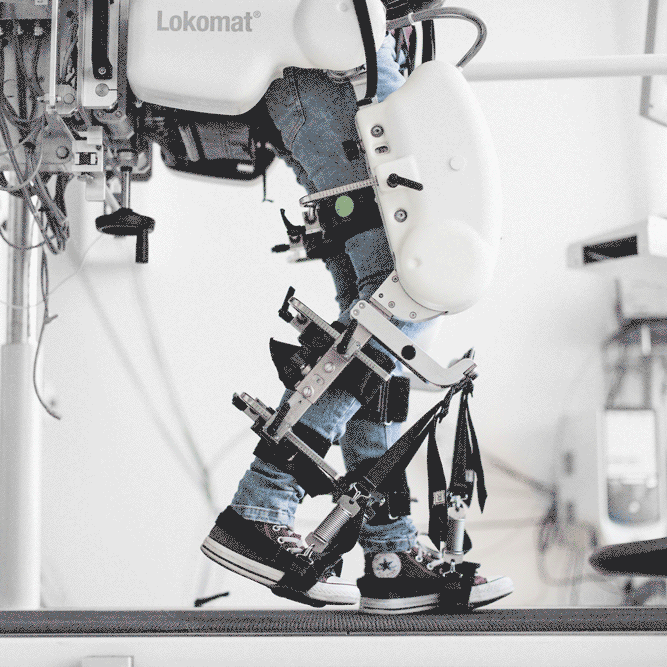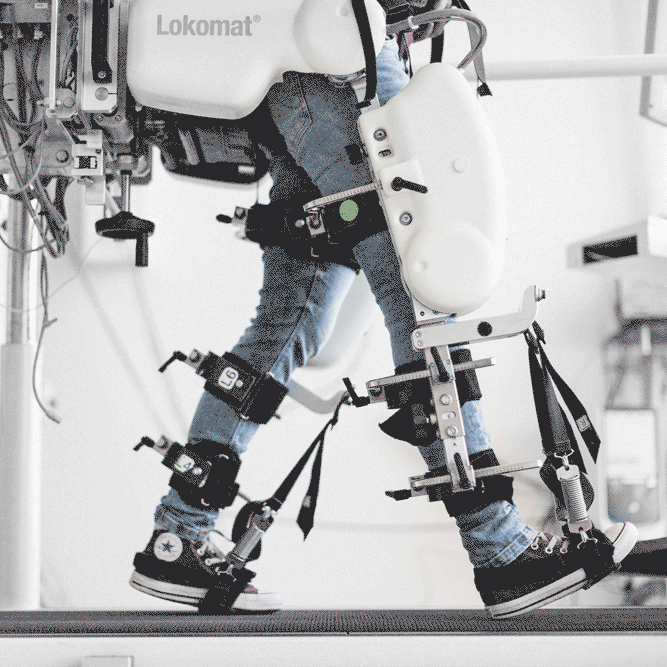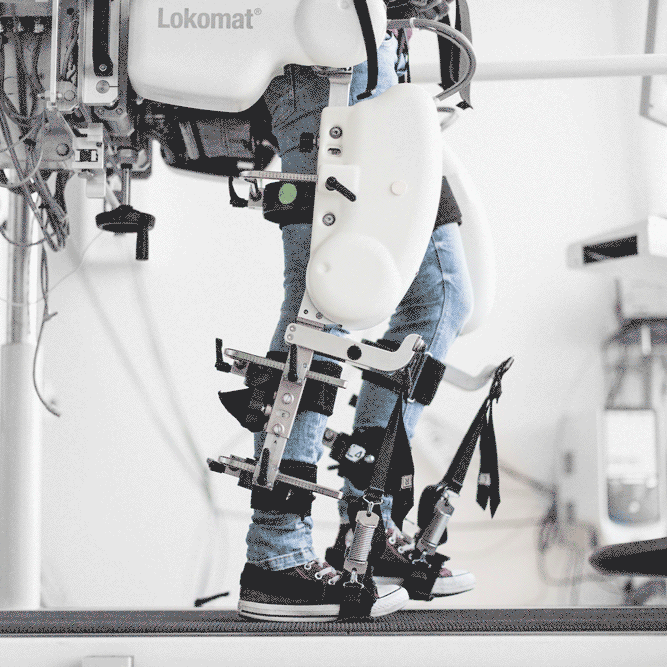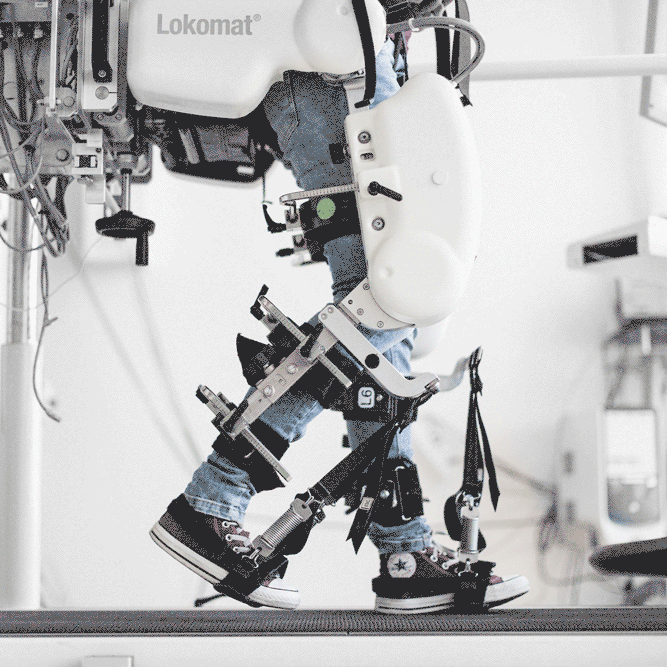
Current research of our group focuses on improving the effectiveness of robot-aided gait training in three ways. First, patient-cooperative control is used so that the robot adapts its behavior to the patient´s needs. Second, additional degrees of freedom for the robotic orthosis allow a more natural walking pattern and last a virtual reality environment is used to maximize the patient’s motivation.
More about Lokomat
